The Concept of Homesteading
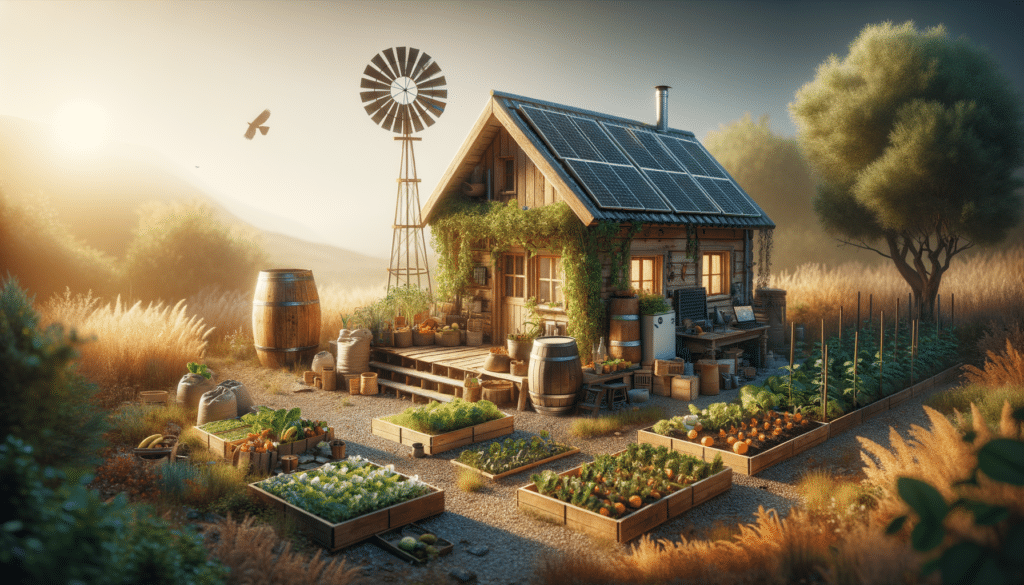
Homesteading is a lifestyle choice that embraces self-sufficiency and sustainability, often through practices such as growing your own food, raising animals, and utilizing renewable resources. This movement has gained traction as individuals seek to reduce their environmental footprint and live more sustainably. The essence of homesteading lies in the integration of traditional skills with modern innovations to create a holistic and balanced way of life.
The roots of homesteading can be traced back to the 19th century, when the Homestead Act of 1862 encouraged Americans to settle and cultivate land. Today, the concept has evolved beyond farming to include a wide array of self-reliant practices. These practices often involve:
- Organic gardening: Growing fruits, vegetables, and herbs without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides.
- Animal husbandry: Raising livestock for meat, dairy, eggs, and other products.
- Renewable energy: Utilizing solar panels, wind turbines, and other green technologies to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Preservation techniques: Canning, fermenting, and dehydrating food to extend its shelf life.
Homesteading not only offers a chance to connect with nature, but it also provides a sense of accomplishment and independence. By producing their own food and energy, homesteaders can reduce their dependence on commercial systems and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Benefits of Homesteading for Sustainable Living
Homesteading offers numerous benefits for those looking to adopt a sustainable lifestyle. One of the most significant advantages is the reduction of environmental impact. By growing their own food, homesteaders can minimize the carbon footprint associated with transporting produce from farm to table. Additionally, organic farming practices help preserve soil health and biodiversity.
Another benefit is the potential for financial savings. Although the initial setup of a homestead can be costly, over time, the reduction in grocery bills and utility costs can lead to significant savings. Homesteaders often find that their investment in renewable energy and sustainable practices pays off in the long run.
Moreover, homesteading fosters a strong sense of community and collaboration. Many homesteaders participate in local farmers’ markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and skill-sharing workshops. These activities not only support local economies but also encourage the exchange of knowledge and resources.
Homesteading also promotes a healthier lifestyle. By consuming fresh, organic produce and engaging in physical labor, homesteaders can improve their physical and mental well-being. The connection to nature and the satisfaction of producing one’s own food contribute to a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Challenges and Considerations in Homesteading
While homesteading offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that must be carefully considered. One of the primary challenges is the time and effort required to maintain a homestead. Homesteading is a labor-intensive lifestyle that demands dedication and perseverance. Prospective homesteaders should be prepared for the physical demands and the learning curve associated with mastering new skills.
Another consideration is the need for adequate space and resources. Not everyone has access to large plots of land, and urban homesteaders may need to get creative with vertical gardening, rooftop gardens, or community plots. Additionally, the initial investment in tools, seeds, livestock, and renewable energy systems can be substantial.
Weather and climate conditions also play a significant role in homesteading success. Unpredictable weather patterns, such as droughts or heavy rains, can affect crop yields and livestock health. Homesteaders must be adaptable and willing to implement strategies to mitigate these challenges, such as rainwater harvesting or crop rotation.
Despite these challenges, many find the homesteading lifestyle to be deeply rewarding. By embracing a sustainable way of living, homesteaders can contribute to environmental conservation, build resilience, and cultivate a meaningful connection to the land.